
7 Mistakes You're Making with Fertilizer for Tomatoes (And the Simple Fix That Changes Everything)
error detected: fertilizer application failure
most tomato plants underperform. system analysis reveals seven critical errors in nutrient delivery protocols.
mistake_001: nutrient oversaturation
fertilizer.exe has encountered an overflow condition. excessive nitrogen loads trigger vegetative subroutines while fruit production modules remain inactive.
symptoms detected:
- leaf mass expansion beyond optimal parameters
- flower abortion rates increase 40-60%
- root system damage from salt accumulation
- heat stress amplification during summer cycles
fix.protocol: reduce input levels to manufacturer specifications. more ≠ better. system requires balanced resource allocation.
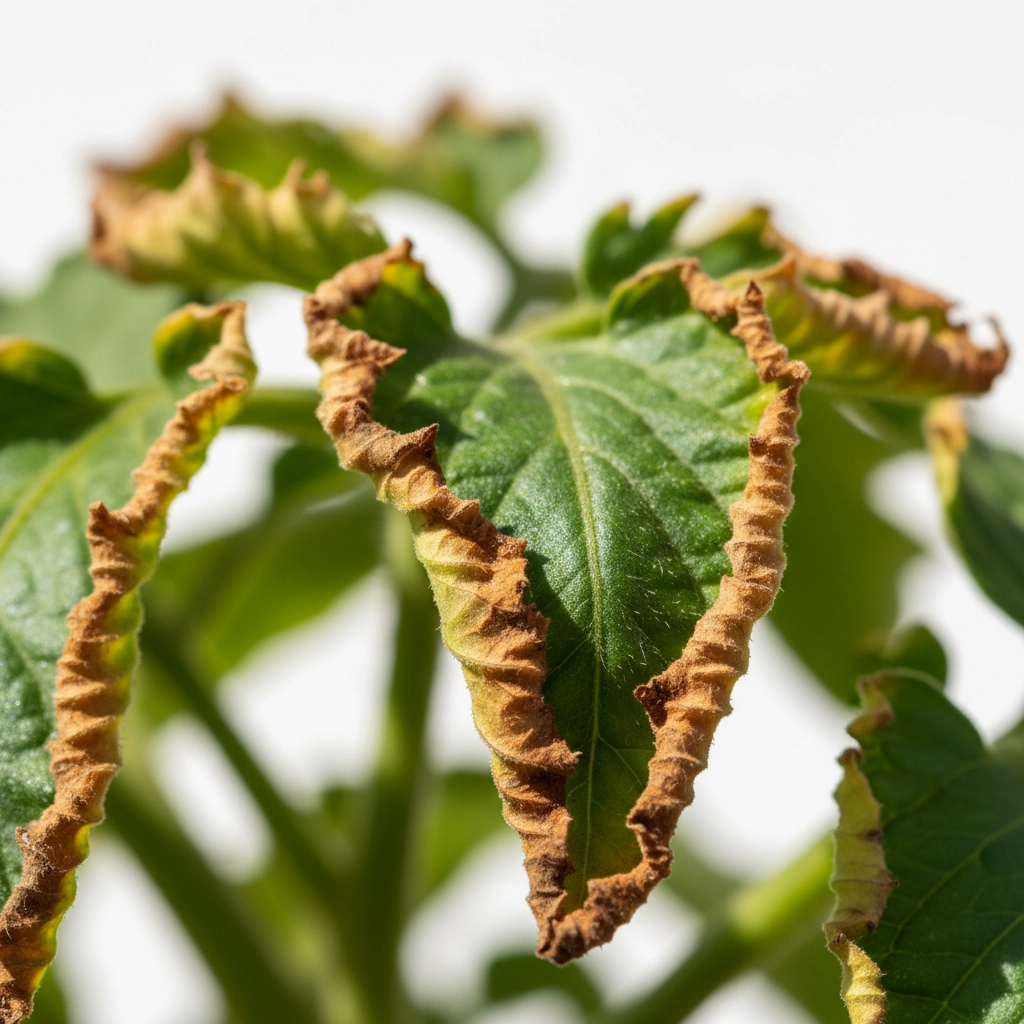

mistake_002: dry soil application error
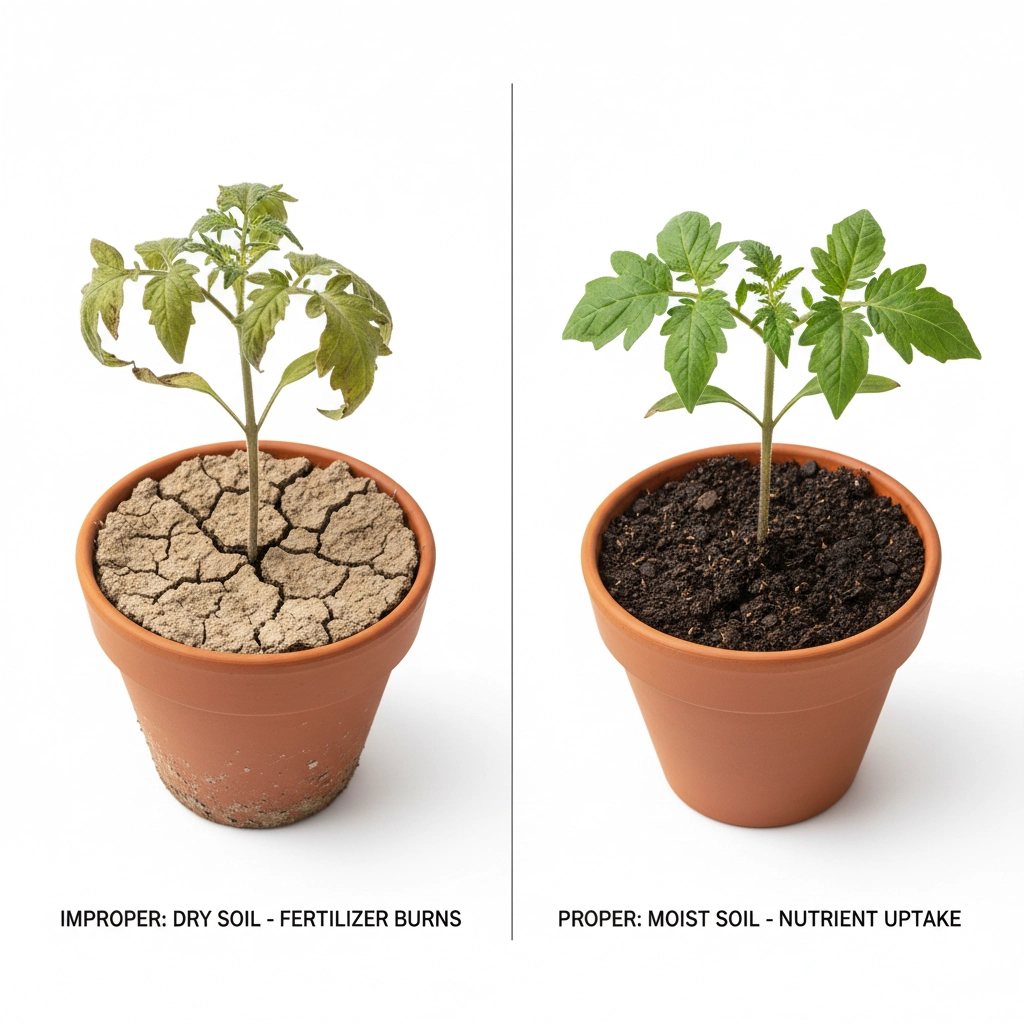
critical system fault: applying concentrated nutrients to dehydrated growing medium causes root burn condition.
error_code: fertilizer_on_dry_substrate_001
synthetic salt concentrations create toxic environment when soil moisture levels drop below threshold. root systems experience thermal damage. plant stress indicators spike during high temperature periods.
fix.protocol:
- execute soil hydration sequence before nutrient application
- wait for natural precipitation events
- verify moisture content at root zone level
water dilutes nutrient concentration. prevents system damage.
mistake_003: incorrect nutrient timing protocol
nitrogen-heavy formulations appropriate during initial growth phase. continuing high-nitrogen feeds during reproductive cycle creates resource allocation error.
plant.priority shifts from fruit development to leaf production. harvest yields decrease substantially.
fix.protocol:
- switch to phosphorus/potassium dominant feeds when flowering initiates
- implement 3-4-4 npk ratio during fruiting phase
- discontinue high-nitrogen applications post flower formation

system requires different resource profiles at different operational stages.
mistake_004: improper application geometry
placing nutrients adjacent to stem causes chemical burns. nutrient distribution patterns fail to reach root network zones.
fix.protocol:
- maintain 3-4 inch buffer from stem base
- distribute fertilizer in circular pattern around drip line
- incorporate into top soil layer 2-3 inches depth
- avoid direct stem contact
nutrients migrate downward through soil profile. root systems access resources efficiently when properly distributed.
mistake_005: insufficient nutrient provisioning
modern tomato cultivars engineered for high output performance. soil nutrient reserves inadequate for maximum productivity.
system requires consistent feeding schedule to maintain optimal function.
fix.protocol:
- establish pre-planting soil amendment routine
- initiate feeding cycle when first fruit sets
- maintain regular application intervals throughout growing season
- adjust formulations based on plant development stage

mistake_006: liquid fertilizer concentration error
undiluted liquid nutrients create root system damage. concentrated solutions overwhelm plant absorption mechanisms.
summer heat amplifies damage potential. fertilizer salt buildup creates hostile growing environment.
fix.protocol:
- follow manufacturer dilution ratios exactly
- measure liquid fertilizer concentrations precisely
- avoid strength modifications
- excess concentration produces plant damage, not larger fruit
mistake_007: nutrient balance system failure
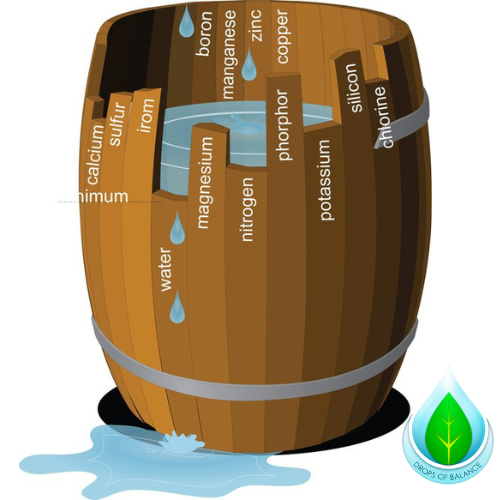
single-element focus creates deficiency cascades. tomato plants require comprehensive mineral profile for optimal function.
calcium deficiency triggers blossom end rot. magnesium shortage causes chlorophyll production errors.
fix.protocol:
- execute soil analysis before planting
- select complete fertilizer formulations
- supplement calcium and magnesium as indicated
- monitor ph levels for nutrient availability
system_override: the comprehensive fix
soil testing eliminates guesswork. strategic feeding protocols replace random nutrient applications.
implementation sequence:
- analyze soil composition and ph levels
- select appropriate fertilizer based on results
- establish watering protocols before nutrient application
- adjust formulations according to plant growth stage
- maintain consistent application intervals
- monitor plant response indicators
water quality affects nutrient uptake efficiency. contaminated water sources reduce fertilizer effectiveness.

trace minerals enhance nutrient absorption. clean water removes chlorine and fluoride interference. proper mineral balance supports plant health systems.
check water treatment solutions
diagnostic_results: performance optimization achieved
implementing proper fertilization protocols transforms plant productivity. systematic approach eliminates common failure points.
key performance indicators improve:
- fruit production increases 25-40%
- plant health status stabilizes
- harvest duration extends
- fruit quality parameters exceed baseline
fertilization becomes predictable science rather than random application process.
system requires:
- soil analysis data
- proper water treatment
- stage-appropriate nutrition
- consistent application protocols
error correction complete. optimal tomato production initialized.
